- Email:[email protected]
- phone:+1 (305) 340-3049
21 Oct
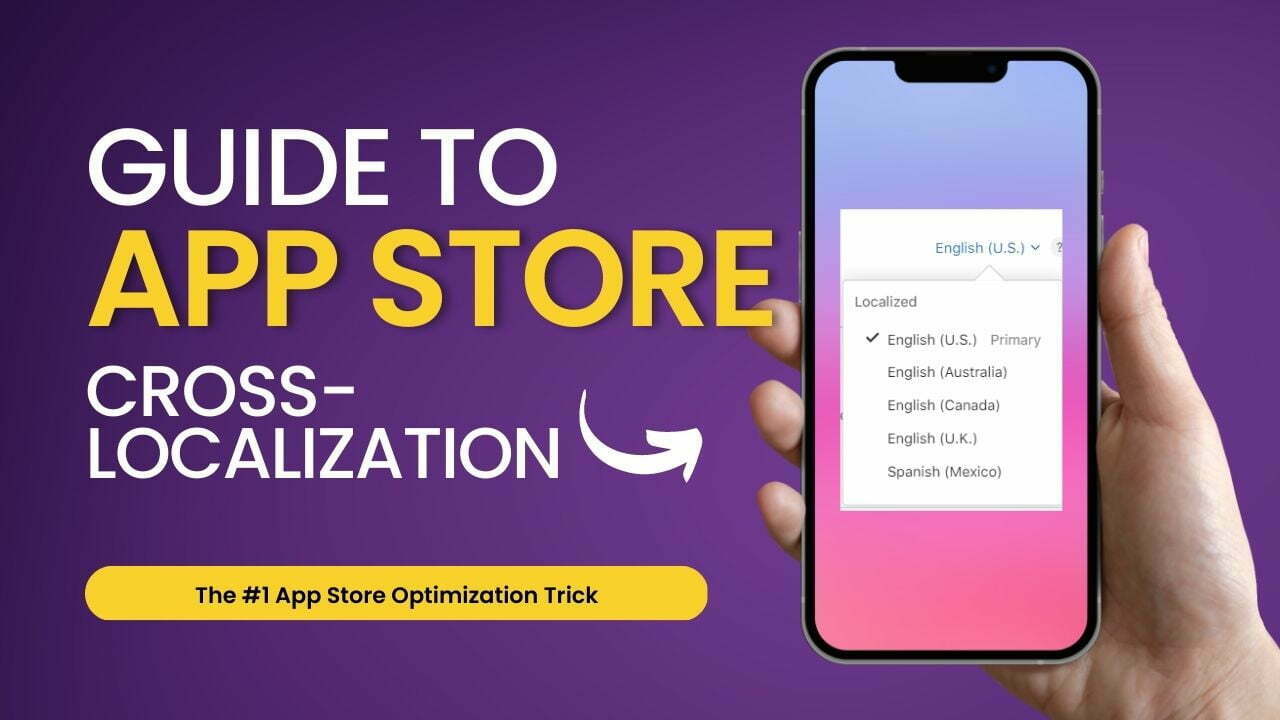
If you’re looking to expand your app’s presence globally and maximize the number of keywords your app ranks for, cross-localization is a must-have strategy. This powerful App Store Optimization (ASO) technique allows you to use more keywords across your app’s metadata by utilizing different App Store locales.
Cross-localization is the App Store Optimization (ASO) trick that lets you use more keywords in your App Store title (30 characters), subtitle (30 characters), and keyword field (100 characters). This powerful ASO technique allows you to increase the character space for your app’s metadata by utilizing metadata in different country App Stores. This is only applicable to the App Store, not Google Play.
Cross-Localization of App Store Territories & Locales (2024)
| COUNTRY | PRIMARY LANGUAGE | LANGUAGES INDEXED |
|---|---|---|
| United States | English (US) | Spanish (Mexico), Russian, Chinese (Simplified), Arabic, French, Portuguese (Brazil), Chinese (Traditional), Vietnamese, Korean |
| United Kingdom | English (UK) | English (Australia) |
| Algeria | Arabic | French, English (UK) |
| Angola | English (UK) | |
| Anguilla | English (UK) | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | English (UK) | |
| Argentina | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Armenia | English (UK) | |
| Australia | English (Australia) | English (UK) |
| Austria | German | English (UK) |
| Azerbaijan | English (UK) | |
| Bahamas | English (UK) | |
| Bahrain | Arabic | English (UK) |
| Barbados | English (UK) | |
| Belarus | English (UK) | |
| Belgium | English (UK) | French, Dutch |
| Belize | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Benin | English (UK) | French |
| Bermuda | English (UK) | |
| Bhutan | English (UK) | |
| Bolivia | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Botswana | English (UK) | |
| Brazil | Portuguese (Brazil) | English (UK) |
| Brunei Darussalam | English (UK) | |
| Bulgaria | English (UK) | |
| Burkina Faso | English (UK) | French |
| Cambodia | English (UK) | French |
| Canada | English (Canada) | French (Canada) |
| Cape Verde | English (UK) | |
| Cayman Islands | English (UK) | |
| Chad | English (UK) | French, Arabic |
| Chile | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| China | Chinese (Simplified) | English (UK) |
| Colombia | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Costa Rica | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Croatia | Croatian | English (UK) |
| Cyprus | English (UK) | Greek, Turkish |
| Czech Republic | Czech | English (UK) |
| Denmark | English (UK) | Danish |
| Dominica | English (UK) | |
| Dominican Republic | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Ecuador | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Egypt | Arabic | French, English (UK) |
| El Salvador | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Estonia | English (UK) | |
| Federated States of Micronesia | English (UK) | |
| Fiji | English (UK) | |
| Finland | English (UK) | Finnish |
| France | French | English (UK) |
| Gambia | English (UK) | |
| Germany | German | English (UK) |
| Ghana | English (UK) | |
| Greece | Greek | English (UK) |
| Grenada | English (UK) | |
| Guatemala | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Guinea-Bissau | English (UK) | French |
| Guyana | English (UK) | French |
| Honduras | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Hong Kong | Chinese (Traditional) | English (UK), Cantonese |
| Hungary | Hungarian | English (UK) |
| Iceland | English (UK) | |
| India | Hindi | English (UK) |
| Indonesia | Indonesian | English (UK) |
| Ireland | English (UK) | |
| Israel | Hebrew | English (UK) |
| Italy | Italian | English (UK) |
| Jamaica | English (UK) | |
| Japan | Japanese | English (US) |
| Jordan | Arabic | English (UK) |
| Kazakhstan | English (UK) | |
| Kenya | English (UK) | |
| Kuwait | Arabic | English (UK) |
| Kyrgyzstan | English (UK) | |
| Lao People’s Democratic Republic | English (UK) | French |
| Latvia | English (UK) | |
| lbania | English (UK) | |
| Lebanon | Arabic | French, English (UK) |
| Liberia | English (UK) | |
| Lithuania | English (UK) | |
| Luxembourg | English (UK) | French, German |
| Macau | Cantonese | English (UK), Chinese (Traditional) |
| Madagascar | English (UK) | French |
| Malawi | English (UK) | |
| Malaysia | Malay | English (UK) |
| Mali | English (UK) | French |
| Malta | English (UK) | |
| Mauritania | Arabic | French, English (UK) |
| Mauritius | English (UK) | French |
| Mexico | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Moldova | English (UK) | |
| Mongolia | English (UK) | |
| Montserrat | English (UK) | |
| Mozambique | English (UK) | |
| Namibia | English (UK) | |
| Nepal | English (UK) | |
| Netherlands | Dutch | English (UK) |
| New Zealand | English (Australia) | English (UK) |
| Nicaragua | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Niger | English (UK) | French |
| Nigeria | English (UK) | |
| North Macedonia | English (UK) | |
| Norway | Norwegian | English (UK) |
| Oman | English (UK) | |
| Pakistan | English (UK) | |
| Palau | English (UK) | |
| Panama | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Papua New Guinea | English (UK) | |
| Paraguay | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Peru | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Philippines | English (UK) | |
| Poland | Polish | English (UK) |
| Portugal | Portuguese (Portugal) | English (UK) |
| Qatar | English (UK) | |
| Republic Of Korea | Korean | English (UK) |
| Republic of the Congo | English (UK) | French |
| Romania | Romanian | English (UK) |
| Russia | Russian | English (UK), Ukrainian |
| Saint Lucia | English (UK) | |
| São Tomé and Príncipe | English (UK) | |
| Saudi Arabia | Arabic | English (UK) |
| Senegal | English (UK) | French |
| Seychelles | English (UK) | French |
| Sierra Leone | English (UK) | |
| Singapore | Chinese (Simplified) | English (UK) |
| Slovakia | Slovak | English (UK) |
| Slovenia | English (UK) | |
| Solomon Islands | English (UK) | |
| South Africa | English (UK) | |
| Spain | Spanish (Spain) | English (U.K.), Catalan |
| Sri Lanka | English (UK) | |
| St. Kitts and Nevis | English (UK) | |
| St. Vincent and The Grenadines | English (UK) | |
| Suriname | Dutch | English (UK) |
| Swaziland | English (UK) | |
| Sweden | Swedish | English (UK) |
| Switzerland | German | English (UK), French, Italian |
| Taiwan | Chinese (Traditional) | English (UK) |
| Tajikistan | English (UK) | |
| Thailand | Thai | English (UK) |
| Trinidad and Tobago | English (UK) | French |
| Tunisia | Arabic | French, English (UK) |
| Turkey | Turkish | English (UK), French |
| Turkmenistan | English (UK) | |
| Turks and Caicos | English (UK) | |
| Uganda | English (UK) | |
| Ukraine | Ukrainian | Russian, English (UK) |
| United Arab Emirates | Arabic | English (UK) |
| United Republic Of Tanzania | English (UK) | |
| Uruguay | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Uzbekistan | English (UK) | |
| Venezuela | Spanish (Mexico) | English (UK) |
| Vietnam | Vietnamese | English (UK) |
| Virgin Islands | English (UK) | |
| Yemen | Arabic | English (UK) |
| Zimbabwe | English (UK) |
Note: The chart has been sourced from Appfollow, Appradar, Phiture, MobileAction, and Sensor Tower.
Why Cross-Localization Matters
With Apple’s App Store, you have limited character space for your title (30 characters), subtitle (30 characters), and keyword field (100 characters). Cross-localization allows you to increase this space by leveraging other countries’ App Stores, effectively expanding your keyword reach. By doing so, you can boost your app’s discoverability without altering the core listing.
This strategy applies only to the App Store, not Google Play.
How to Use Cross-Localization Effectively
- Research Indexed Languages: Tools like AppFollow and SensorTower help identify which languages are indexed in different countries. This allows you to optimize your app’s metadata for various locales.
- Avoid Keyword Duplication: Ensure that keywords from one localization aren’t repeated in another. Duplicating keywords won’t improve your ranking and wastes valuable keyword space.
- Leverage Dialect Variations: English (UK) and English (US) are considered separate localizations. This means you can use “color” in one and “colour” in another without violating duplication rules.
- Maximize Exchangeable Localizations: Some localizations are interchangeable across regions. For instance, if French (Canada) isn’t available in a country, French (France) metadata may still be indexed.
- Consider the Target Audience: Always optimize secondary localizations with relevant keywords specific to that audience. For example, using local slang or cultural references can improve your app’s performance in that market.
Case Study: Cross-Localization in Action
Let’s look at an example. You’ve developed a fitness app called “FitLife,” and it’s performing well in the U.S. market. To expand your keyword space, you decide to add a Spanish (Mexico) localization to your U.S. listing, which allows you to use English keywords in the secondary localization. As a result, your app’s visibility improves, and you start reaching a larger audience of English-speaking users.
Ready to Implement Cross-Localization?
If managing cross-localization feels overwhelming, Outrank Apps is here to help. Our ASO experts can handle the entire process, ensuring your app reaches new audiences in global markets. Contact us today for a free consultation and learn more about how cross-localization can boost your app’s success.


Jason Batansky